
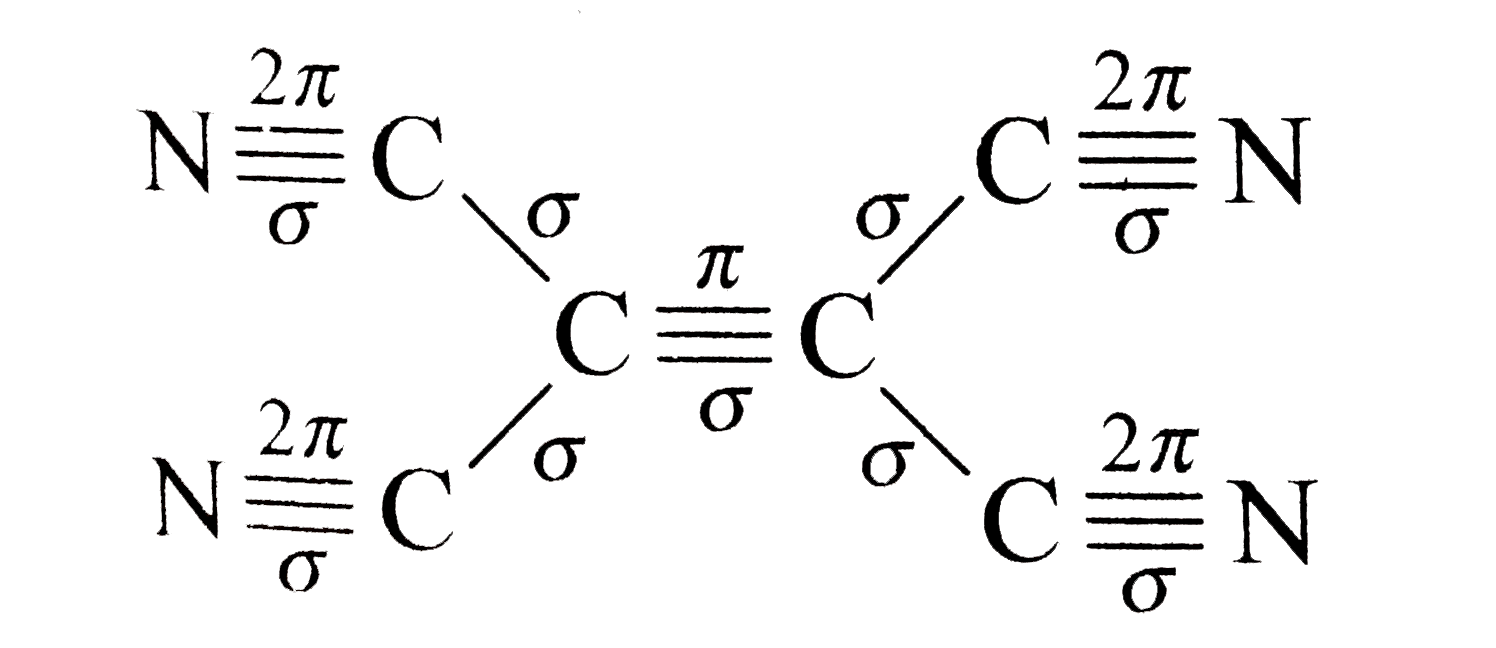
There is no more than 1 sigma bond between any two atoms. This rule is a special-case application of the Euler characteristic of the graph which represents the molecule.Ī molecule with no rings can be represented as a tree with a number of bonds equal to the number of atoms minus one (as in dihydrogen, H 2, with only one sigma bond, or ammonia, NH 3, with 3 sigma bonds).
Ch2nn sigma and pi bonds plus#
According to the sigma bond rule, the number of sigma bonds in a molecule is equivalent to the number of atoms plus the number of rings minus one. Organic molecules are often cyclic compounds containing one or more rings, such as benzene, and are often made up of many sigma bonds along with pi bonds. These sigma bonds can be supplemented with other bonding interactions, such as π-back donation, as in the case of W(CO) 3( PCy 3) 2(H 2), and even δ-bonds, as in the case of chromium(II) acetate. Transition metal complexes that feature multiple bonds, such as the dihydrogen complex, have sigma bonds between the multiple bonded atoms. For example, propane is described as consisting of ten sigma bonds, one each for the two C−C bonds and one each for the eight C−H bonds. The concept of sigma bonding is extended to describe bonding interactions involving overlap of a single lobe of one orbital with a single lobe of another. Overall this sigma-pi picture of the double bond is reminiscent of a hot dog in a bun.Sigma bonds are obtained by head-on overlapping of atomic orbitals. Because the pi bond has less electron density between the atoms, it is of higher energy in the MO diagram and is weaker than the sigma bond. In 3D, this linear node would be a plane, separating the two lobes of high electron density that constitute the pi bond. The m 2,1 mode has a linear node between the atoms, and maximum amplitude in front of, and behind, the node, representing the pi bond. The m 1,0 mode has no nodes, so the maximum amplitude of the standing wave is between the atoms, representing a high electron density sigma bond. Imagine the two atoms opposite one another where a diagonal meets the edge of the drum at extreme left and right points. This node is akin to the shape of the pi bond where there is no electron density along the plane.Īlternatively, we can envision the molecular orbitals with the Drum Model described earlier. (b) The second-lowest energy standing wave has a single node. This is like the continual electron density in all directions around the sigma bonding orbital. (a) The lowest energy form of a standing wave has no nodes. Thus the pi molecular orbital is higher in energy and is the highest occupied molecular orbital (the HOMO).
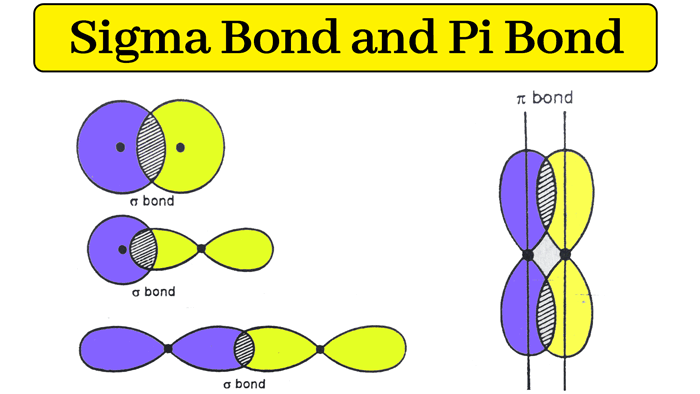

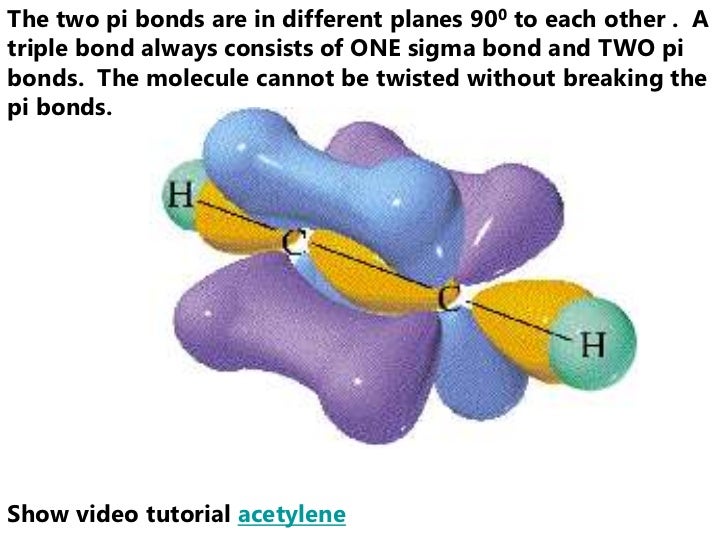
The pi bond between the two carbon atoms has one node in the plane of the molecule. The sigma bond between the two carbon atoms does not have a node in the plane of the molecule. The wave with a single node has higher energy. If your workstation is enabled for JCE Software, you will see two videos below which compare the behavior of a standing wave with zero nodes versus a standing wave with one node (otherwise, see the drum animation below). The pi bond can be thought of as a standing wave with a single node in the plane of the molecule. Each of the two electrons in the pi bond (π bond) exists both above and below the plane of the four H atoms and the two C atoms. The pi bond (π bond) has two halves-one above the plane of the molecule, and the other below it. This is called a pi bond, Greek letter π. A second carbon-carbon bond is formed by the overlap of these two remaining p orbitals. The sp2 hybrid orbitals on each carbon atom involve the 2 s and two of the 2 p orbitals, leaving a single 2 p orbital on each carbon atom. By selecting N8 HOMO, you can see the pi orbital represented by the two lobes. This is actually sigma bonding between C-C and some sigma-like bonding around the Hs as well. To view the sigma bonding orbital, select N6. These overlap sideways to form a π bond, also shown in gray. Two p orbitals, one on each C atom, are shown in gray. Two of these overlap directly between the carbon atoms to form the σ bond. Three sp 2 hybrids around each carbon atom are indicated in color.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
